The calorific value (CV) of a fuel is a characteristic of fuel which is defined as the energy liberated per kg of fuel burnt. Fuels are found in three-phase viz. solid, liquid, and gaseous. Junker’s calorimeter is used to measure the CV of gaseous fuels. This article helps you to know the process to determine the calorific value of a fuel with the help of a bomb calorimeter.
Bomb Calorimeter experiment:
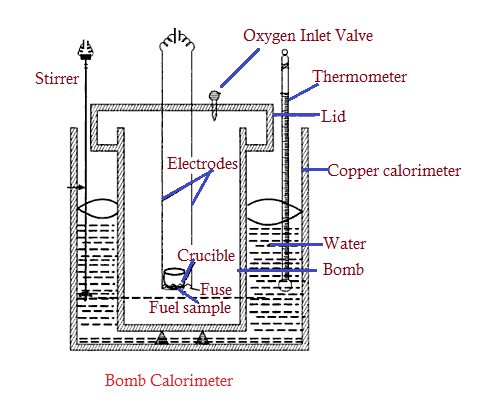
- It is used to measure the calorific value (CV) of a solid as well as a liquid fuel. But to determine the CV of gas, one needs to choose Junker’s calorimeter.
- A calorimeter contains a thick-walled cylindrical vessel and it consists of a lid that supports two electrodes that are in contact with the fuse and fuel sample of known weight.
- The lid also contains an oxygen inlet valve through which high-pressure oxygen gas (at about 25 to 30 atm) is supplied.
- The entire lid with a fuel sample is now held in a copper calorimeter containing a known weight of water. A mechanical stirrer is provided to stir well for uniform heating of water.
- A thermometer is also provided to measure the change in temperature of water due to the combustion of fuel in the Lid.
The procedure of the Bomb Calorimeter experiment
- A known quantity of fuel sample is added to the crucible.
- Start the stirrer and note down the initial temperature of the water.
- Start current through the crucible and let the fuel sample burn in the presence of oxygen.
- The heat released during the combustion of fuel is taken by water and hence the temperature of water rises.
- Note the final steady-state temperature of the water.
Higher Calorific Value of fuel = (m1+m2) x (Tc + T1 – T2 ) x Cw / mf
Where,
m1 and m2 are the mass of water in the copper calorimeter and the water equivalent of the bomb calorimeter respectively, mf is the mass of the fuel sample whose calorific value is to be determined.
T1 and T2 are the final and initial temperatures of the water sample. Tc is temperature correction for radiation losses. Cw is the specific heat of the water
The water equivalent of a bomb calorimeter can be found for a particular bomb calorimeter by first doing an experiment based on a known fuel sample whose calorific value is already known. It depends on the manufacturer of the Bomb calorimeter.
Practical applications of Bomb Calorimeter:
Bomb Calorimeter is used for the measurement of the calorific value of fuel oils, gasoline or petrol, coke, coal, combustion waste, foodstuffs, building materials, etc. A bomb calorimeter is also used for energy balance study in ecology and the study of Nano-material, ceramics, and zeolite. The bomb calorimeter is helpful to study the thermodynamics of common combustible materials.